The State of Corrections in Georgia
Every Georgian is affected by the criminal justice system in some way. Whether it is paying taxes to fund the more than a billion dollars spent on prisons each year or knowing a loved one who has spent time behind bars, the justice system is becoming an increasingly familiar issue in the lives of Georgians.
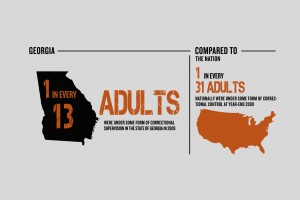
In 2009, the Pew Center on the States released a report revealing that 1 in 13 adults were under some form of correctional supervision in Georgia. This means that over half-a-million Georgians were either in jail, in prison, on parole, or on probation that year. This percentage far surpassed the national average, which was still an astonishing 1 in 31 adults under correctional supervision.
Even more staggering, 2.6 million people have a criminal record on file with the Georgia Crime Information Center, while the state’s total population is 10 million people. The collateral consequences associated with having a criminal record mean that as many as 1 in 4 Georgians likely face barriers to obtaining employment, housing, and even voting.
Currently, 53,000 people are incarcerated in Georgia, giving the state the fifth highest prison population in the nation. The incarcerated population more than doubled between 1990 and 2011, while the state’s general population increased by only half that rate during the same time period.
The Merry-Go-Round
Once a person enters the system, his or her likelihood of staying in it is fairly strong. The state releases 20,000 prisoners back into the community every year, and 2 out of 3 of those released are rearrested within three years. Nearly 1 in 3 are re-convicted within this time frame, resulting in re-incarceration.
While the state reports a recidivism rate of 30 percent over the past decade (determined by the number of offenders who are reconvicted within three years of release), the actual recidivism rate is closer to 50 percent – taking into account the number of people who commit a technical violation while on probation and parole, as well as the number of offenders who recidivate after the standard three-year time period.
The Cost
The effect of recidivism is very costly to the state: It negatively impacts public safety, results in burgeoning costs to taxpayers, and contributes to the breakdown of families.
Public Safety
Released offenders who continue to have unaddressed criminogenic (crime-producing) needs are likely to re-engage in criminal behavior and place themselves, their families, and their community at risk. Criminal behavior may arise from a substance abuse or mental health issue, from negative peer associations, from a poor family environment, from desperation caused by their inability to meet their basic needs for housing, employment, and transportation, and from a variety of other risk factors. Without addressing the underlying factors that lead returning citizens to engage in criminal behavior, the recidivism rate will continue to remain high as new crimes and technical violations of probation and parole are committed.
Taxpayers
Recidivism places a heavy burden on taxpayers. The cost to incarcerate one person for a year in Georgia is $21,000 – more than twice the amount the state spends toward educating one student for a year. This means that every cohort of released prisoners that recidivates amounts to $130 million annually, given the 30 percent recidivism rate and the 20,000 offenders released each year. Further, state expenditures on incarceration reached $1.1 billion in fiscal year 2010 – more than twice the amount spent in 1990, which was $492 million. For the amount taxpayers have spent on the prison system in recent years, the outcomes have been unacceptable.
Families
Finally, a person cycling in and out of prison creates instability in the life of his or her family. Significantly, 60 percent of inmates in Georgia are parents, and a number of these parents have been incarcerated more than once. Children of incarcerated parents are more likely to perform poorly in school, to be exposed to their parent’s substance abuse, to use drugs, to experience mental health issues, to experience domestic violence, and to live in poverty. Incarceration puts a tremendous strain on existing relationships, decreases the chances that partners will marry, transforms family roles, and often leads custodial parents to depend on public assistance. Families experience shame, anger, hurt, and despair at the incarceration of loved ones, creating inner turmoil that is often never addressed.
What Can Be Done?
Because of the enormous costs posed by incarceration and recidivism, it is essential for Georgia to promote solutions that will address underlying issues returning citizens face. This effort must take place at all points along the continuum, from the Governor’s Office down to individuals in the community.
Several areas of reform that Georgia Center for Opportunity’s Prisoner Reentry Working Group has addressed to improve reentry outcomes involve increasing employment opportunities (read report), restructuring debt, and developing the criminal justice and service provider workforce.
Employment
Employment plays a critical role in reducing offender recidivism, as it has the power to deter ex-offenders from crime and incentivize law-abiding behavior. Key barriers to employment that the working group identified include driver’s license suspensions, missing identification (i.e., Social Security cards and birth certificates), professional license restrictions, and employers’ negative perceptions.
To remove these barriers, the group recommended that the state lift suspensions on driver’s licenses for people who committed a non-driving related drug offense, offer incentives to employers to hire those with a criminal record, and have public and private employers postpone the question about an applicant’s criminal history to a later point in the interview process. Several of these recommendations were signed into law in April 2014.
Debt
Various state agencies enforcing the payment of debts and obligations without considering the needs and financial circumstance of returning citizens can lead them to recidivate. Returning citizens often carry excessive debt because of missed child support payments that accrue during their incarceration, court-imposed fees, fines, and surcharges for their offense, unpaid restitution, and the inability for them to earn money while in prison.
Several steps that the state can take to encourage returning citizens to repay this debt in a realistic manner include: Identifying offenders with child support orders upon entry to prison; providing offenders with pertinent information about their child support responsibilities; providing a grace period of 90 days upon release that gives returning citizens the opportunity to find a job and get back on their feet; and providing incentives for returning citizens to pay current obligations of child support and restitution by forgiving a portion of fines, fees, surcharges, and child support arrears owed to the state.
Workforce Development
There is an urgent need for the criminal justice workforce and community service providers to be trained in delivering evidence-based programs and practices. Without proper training and implementation, Georgia’s recidivism rate is likely to remain unchanged.
The state can better ensure successful reentry outcomes are reached by providing training and support to agencies and service professionals in the use of evidence-based practices, developing a hybrid degree program that combines criminal justice training and case management techniques, ensuring a risk/needs assessment is used and followed from entry into prison to treatment in the community, providing the workforce the ability to use graduated sanctions and incentives, and providing accountability to the workforce to ensure evidence-based practices are being used.
Conclusion
Each person involved with this reentry effort, from the governor to mentors in the community, need to put into practice what has shown to work in reducing recidivism. This effort will require education, training, resources, and coordination on all fronts, and it is one that should be pursued with fidelity. Doing so will help to bring restoration to families, build stronger communities, and ensure a more just society.
Click here to view The State of Corrections infographic